Model hyperparameters and model parameters have been used interchangeably in online platforms. It is confusing for many people who are less seasoned in machine learnig area. Eventhough two words replace each other in formal and informal conversations, there is a clear distiction in between based on their role and interaction in machine learning process.
!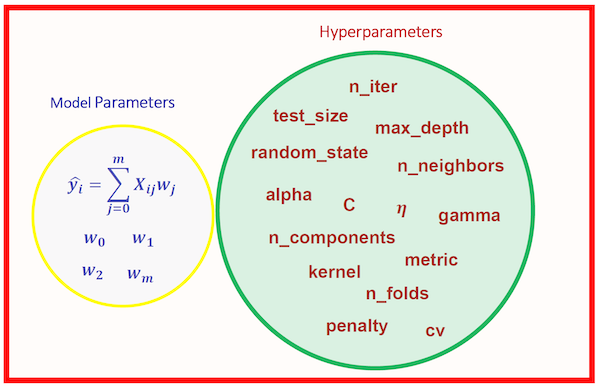
Hyperparameters are values decided outside of model training process whereas parameters are found out during the model training. We built the model with a set of hyperparameters and feed it with the data. At the end of fitting, Aka training, it produces parameters. Another important point of distinction is that, prediction is based on model parameters and not the hyper-parameters.
Parameters
Parameters are some of the products of machine learning process. The model figures out and has them ready to use in prediction at the end of the training. The word of ‘fitting’ ican be interpreted as figuring the parameters for the particular dataset that passed to the model.
Each model has various paramters and it figure those parameter values during training process. This trained model is just like a blueprint that adjusted for a number of instances of a product. It becomes a general blueprint after so many adjustments. A similar product, which was not introduced before, is passed to the bluprint. And see how it fits. Those products are our data instances. Paramters define the structure and shape of the model. It is expected to have a general model eventhough it has some error (loss function) in the training data to have a better fit on the testing data. More or less every machine learning algorith has parameters.
Examples;
Linear regression model; Weights or Coefficients of independent variables
Support Vector Machines Weights or Coefficients of independent variables
Random Forest Decision Tree Split points
We have no inference in the learning process of these parameters. However, hyperparamater values have direct influence in the fitting process hence figuring parameters.
Hyperparameters
Hyper-parameters are those, which we supply to the model. They are often referred to as parameters because they are the parts of the machine learning that must be set manually and tuned. Hyperparameters cannot be learned within the estimator directly. However, ‘parameters’ is more general term. Generally, the expression of ‘passing the parameters to the model’ means a combination of hyperparameters along with some other parameters that are not directly related to your estimator but are required for your model. Model hyper-parameters are used to optimize the model performance. The value of a hyperparameter has to be decided before we train the model.
Examples;
k-means clustering Number of clusters expected
Random Forest Model:
Number of trees to be used
Numbers of features to be used
The distinction between parameters and hyper-parameters is nuanced due to the way they are utilized by data scientists when designing the model and loss-function.
Hyperparameter Tuning
The hyper-parameters are not ‘learnt’ during training, but does not mean their values are final. Typically, the hyper-parameters are fixed and we think that it’s the model. However the hyper-parameters can also be considered as parameters. Because, they can also be changed during training for optimization purposes. An example would be to change the learning-rate during training to improve speed and/or stability of the optimization routine.
Hyperparameter tuning is an important step in Machine Learning or Data science model building process. A good tuning would improve the model predictions significantly. Each model has multiple hyperparameters and they all have default values. But, that set of values are not always the best fit for the data. To get the best performance accuracyl, we need to pass the best hyperparameter values to the model.
The question is, how to find the values of hyperparameter or in other words how to do hyperparameter tuning.There is no magic way or quick quick aswer. The values of the hyperparameters are selected using cross validations.
Two most common methods are Manually or Grid Search.
Hyperparamters tuning is mostly a time-consuming process. Figuring best hyperparamters requires massive number of trial and error adjustments. It also a serios load of work on the memory of computers.
How many trial and error?
The number of trial and error during hyperparameter tuning increases geometricly. If you have three values on five parameters to do grid shearch that means you will end up 3x3x3x3x3 = 283 different combinations of these parameters to test. On top of that, the selection process is done using cross validation. That means another multiplier comes in to the scene. Suppose cv=5 for your grid search, then the number of trial and error adjustments will be 285x5=1415. If the dataset is considerably big, then the processing load on the memory and time increases dramaticaly.
The balance between the perfect fit for hyperparameters and the work-load is crucial in tuning process. Data scientists, who has good intuition of the data and the model, carefully chooses the minimum number of ideal candidate values for each hyperparameters. EDA (Exploratary Data Analysis ) is essencial to get good undertanding of the data. On the other hand, well comprehension of models and their hyperparameters are also necessary to choose minimum best candidates for hyperparmater values.
Recently, Some applications, such as Vizier also make grid search autonomus. Google Vizier makes the recipe millions of times, noting potentially thousands of differences when hyperparameters are changed. The network does this until some best solution is found, as originally defined by humans. However, the tuning algorithm is also a black box—this method gives no insight into biases it might instill into the original neural network. But handling such important job is quite valuable in machine learning as the quality and speed of the model is depending on the result of the tuning process.
What makes the difference between a good and a bad machine learning model depends on one’s ability to understand all the details of the model including knowledge about different hyperparameters and how these parameters can be tuned in order to obtain the model with the best performance. Using any machine learning model as a black box without fully understanding the intricacies of the model will lead to a falsified model.
References
https://qz.com/1053431/google-tested-its-ai-by-having-it-fine-tune-chocolate-chip-cookie-recipes/
https://towardsdatascience.com/model-parameters-and-hyperparameters-in-machine-learning-what-is-the-difference-702d30970f6