
A machine learning model that can provide insights by automatically analyzing product reviews and separating them into tags: Positive, Negative with 91% Accuracy
Customer Experience (CX) is the key to business success. In fact, 81% of marketers interviewed by Gartner said they expected their companies to compete mostly on the basis of CX in two years time, making CX the new marketing battlefront. Now, more than ever, it’s key for companies to pay close attention to Voice of Customer (VoC) to improve the customer experience. By analyzing and getting insights from customer feedback, companies have better information to make strategic decisions, an accurate understanding of what the customer actually wants and, as a result, a better experience for everyone.
This machine learning model can provide insights by automatically analyzing product reviews and separating theLoading and Pre-processingm into tags: Positive and Negative. By using sentiment analysis to structure product reviews, you can:

- Understand what your customers like and dislike about your product.
- Compare your product reviews with those of your competitors.
- Get the latest product insights in real-time, 24/7.
- Save hundreds of hours of manual data processing.
Dataset:
I use ‘Amazon Product Reviews Dataset’ from Kaggle. This dataset consists of total 4 millions Amazon customer reviews (input text) and star ratings (output labels).
https://www.kaggle.com/bittlingmayer/amazonreviews
Methodology:
CRISP-DM (Cross Industry Standard Process for Data Mining)
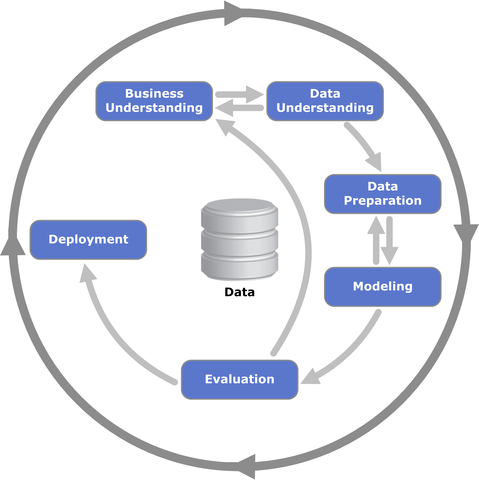 The process or methodology of CRISP-DM is described in these six major steps
The process or methodology of CRISP-DM is described in these six major steps
1.Business Understanding
Focuses on understanding the project objectives and requirements from a business perspective, and then converting this knowledge into a data mining problem definition and a preliminary plan.
2.Data Understanding
Starts with an initial data collection and proceeds with activities in order to get familiar with the data, to identify data quality problems, to discover first insights into the data, or to detect interesting subsets to form hypotheses for hidden information.
3.Data Preparation
The data preparation phase covers all activities to construct the final dataset from the initial raw data.
4.Modeling
Modeling techniques are selected and applied. Since some techniques like neural nets have specific requirements regarding the form of the data, there can be a loop back here to data prep.
5.Evaluation
Once one or more models have been built that appear to have high quality based on whichever loss functions have been selected, these need to be tested to ensure they generalize against unseen data and that all key business issues have been sufficiently considered. The end result is the selection of the champion model(s).
6.Deployment
Generally this will mean deploying a code representation of the model into an operating system to score or categorize new unseen data as it arises and to create a mechanism for the use of that new information in the solution of the original business problem. Importantly, the code representation must also include all the data prep steps leading up to modeling so that the model will treat new raw data in the same manner as during model development.
Notebooks
There are 3 notebooks for this project. I chuncked the project into 3 small pieces. Saved processed data, tokens, vectors and models with pickles to use in the following notebooks.
-
Reading, Pre-processing and EDA
load_preprocess_data.ipynb consists of functions and code to read the data, remove punctuations, remove stopwords, lemmatize, tokenize and vectorize. There is also section for EDA.
Data Understanding and Data Preperation phases for CRISP-DM can be found in this noteboook.
Table of Content:
- 1.Import Libraries
- 2.Define Functions
- 3.Load-Read-Extract
- 4.Pre-Processig
- 5.Tokenizing-Sequenzing-Padding
- 6.Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Train and test data consist 4 millions of reviews. You will not see the datasets or tokens on GitHub because of their size. I uploded preprocessed data to Kaggle. You can download it from the following link.
https://www.kaggle.com/fcamuz/amazon-comments-preprosessed/settings
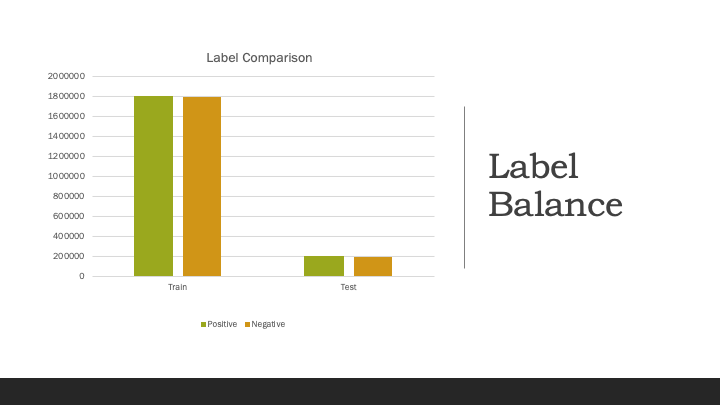
Label distribution is important when it comes to the performence of a model. Unbalanced labels might be a negative effect. But out dataset is perfectly blanced.
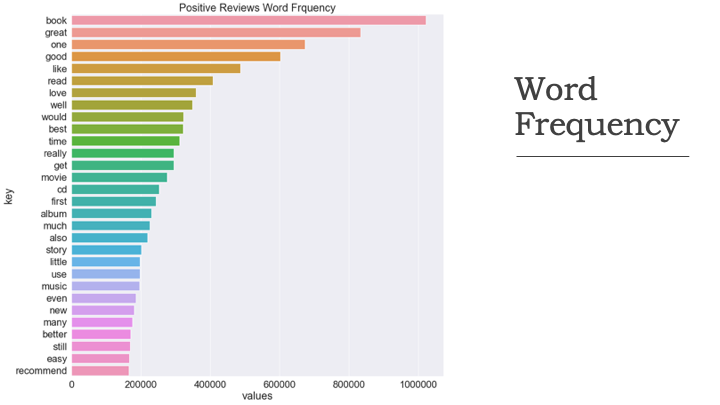
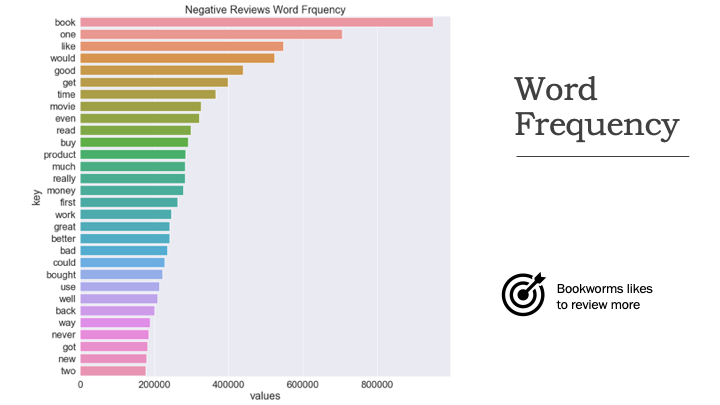
The results for word distributions on negative and positive comments are below. These charts show the most common 30 words for each class.
The average total number of words in comments from each category is below. The difference is small but worth to pay attantion.
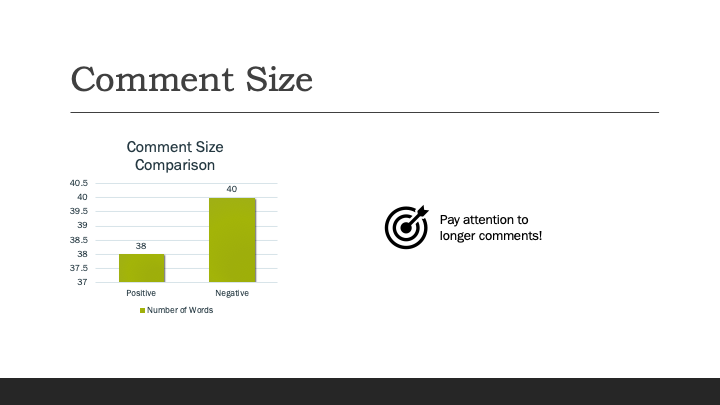
-
Modelling and Evaluation
model.ipynb has all base models train and test results. Tuning for best performing model is also available in this notebook.
Modelling and Evaluation phases for CRISP-DM can be found in this noteboook.
Table of Content:
- 1.Import Libraries
- 2.Define Functions
- 3.Modeling With Neural Networks
- 4.Tuning the Best Model
After I have run 4 different models I chose to use Convolutional Neural Network model because it gave the best accuracy result on training and testing data.
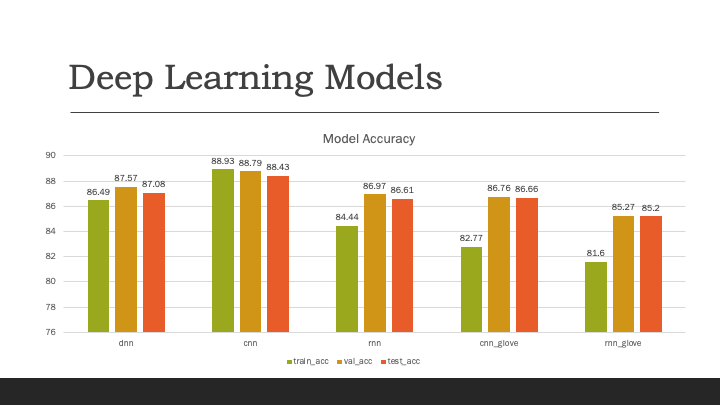
For tunign CNN model, I have have tried:
- Optimizers : SGD, ADAM
- Hidden layers : 1 convolution layer, 2 convolution layers
- Embedding layers weights: Glove embedding, None
- Epochs : 1-10
- Data : Sample dataset (train:150,000, test:30,000), full dataset (train:3,600,000, test:400,000)
Model performed best with CNN with “Adam” optimizer, 2 convolution layers, no Glove embedding and 5 epochs.
After I determined these parameters, I have upload the full pre-processed data to Kaggle and train the model with full dataset
# number of unique words we want to use
max_features = 8192
# max number of words in a comment to use (or: number of columns in incoming embedding vector)
max_len = 128
# dimension of the embedding variable (or: number of rows in output of embedding vector)
embedding_dims = 64
# instantiate CNN model
cnn_2cnv = Sequential()
# add embedding layer
cnn_2cnv.add(Embedding(input_dim=max_features, input_length=max_len,
output_dim=embedding_dims))
# set the dropout layer to drop out 50% of the nodes
cnn_2cnv.add(SpatialDropout1D(0.5))
# add convolutional layer that has ...
# ... 100 filters with a kernel size of 4 so that each convolution will consider a window of 4 word embeddings
cnn_2cnv.add(Conv1D(filters=100, kernel_size=4, padding='same', activation='relu'))
# add normalization layer
cnn_2cnv.add(BatchNormalization())
# add convolutional layer that has ...
# ... 100 filters with a kernel size of 4 so that each convolution will consider a window of 4 word embeddings
cnn_2cnv.add(Conv1D(filters=100, kernel_size=4, padding='same', activation='relu'))
# add normalization layer
cnn_2cnv.add(BatchNormalization())
# add pooling layer
cnn_2cnv.add(GlobalMaxPool1D())
# set the dropout layer to drop out 50% of the nodes
cnn_2cnv.add(Dropout(0.5))
# add dense layer to produce an output dimension of 50 and using relu activation
cnn_2cnv.add(Dense(50, activation='relu'))
# finally add a dense layer
cnn_2cnv.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
cnn_2cnv.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=Adam(0.01),
metrics=['accuracy'])
cnn_2cnv.summary()
Model: "sequential_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
embedding_1 (Embedding) (None, 128, 64) 524288
_________________________________________________________________
spatial_dropout1d_1 (Spatial (None, 128, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv1d_1 (Conv1D) (None, 128, 100) 25700
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_1 (Batch (None, 128, 100) 400
_________________________________________________________________
conv1d_2 (Conv1D) (None, 128, 100) 40100
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_2 (Batch (None, 128, 100) 400
_________________________________________________________________
global_max_pooling1d_1 (Glob (None, 100) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 100) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 50) 5050
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 51
=================================================================
Total params: 595,989
Trainable params: 595,589
Non-trainable params: 400
cnn_2cnv_hist = cnn_2cnv.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size=512,
epochs=5, validation_split=0.1)
Train on 3240000 samples, validate on 360000 samples
Epoch 1/8
3240000/3240000 [==============================] - 3219s 994us/step - loss: 0.2760 - accuracy: 0.8817 - val_loss: 0.2206 - val_accuracy: 0.9118
Epoch 2/8
3240000/3240000 [==============================] - 3235s 998us/step - loss: 0.2331 - accuracy: 0.9061 - val_loss: 0.2106 - val_accuracy: 0.9157
Epoch 3/8
3240000/3240000 [==============================] - 3257s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2251 - accuracy: 0.9099 - val_loss: 0.2124 - val_accuracy: 0.9157
Epoch 4/8
3240000/3240000 [==============================] - 3184s 983us/step - loss: 0.2199 - accuracy: 0.9121 - val_loss: 0.2029 - val_accuracy: 0.9193
Epoch 5/8
3240000/3240000 [==============================] - 3294s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2164 - accuracy: 0.9137 - val_loss: 0.2015 - val_accuracy: 0.9201
cnn_2cnv_loss, cnn_2cnv_auc = cnn_2cnv.evaluate(X_test, y_test, batch_size=32)
print('Test Loss: ', cnn_2cnv_loss)
print('Test Accuracy:', cnn_2cnv_auc)
The model has 91% Accuracy on test set.
-
Prediction
prediction.ipynb consists the pipeline structure for scraping unseen data from Amazon website, pre-processing comments and predicting the labels.
Deployment phase for CRISP-DM can be found in this noteboook.
Table of Content:
- 1.Import Libraries
- 2.Define Functions
- 3.Scraping Comments
- 4.Pre-processing the New Data
- 5.Prediction
I have used urllibmodule and BeatifulSoup library to scrape data from Amazon product webpage. Then I also pre-processed the new text to pass to the model for prediction.
def scrape_reviews ():
# For ignoring SSL certificate errors
ctx = ssl.create_default_context()
ctx.check_hostname = False
ctx.verify_mode = ssl.CERT_NONE
url=input("Enter Amazon Product Url- ")
html_page = urllib.request.urlopen(url) #Make a get request to retrieve the page
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_page, 'html.parser')
reviews=[]
ratings=[]
review_row=soup.findAll('div', attrs={'data-hook': 'review'})
for row in review_row:
ratings.append(row.find('span', attrs={'class':'a-icon-alt'}).text.strip()[0])
reviews.append(row.find('div', attrs={'data-hook': 'review-collapsed'}).text.strip())
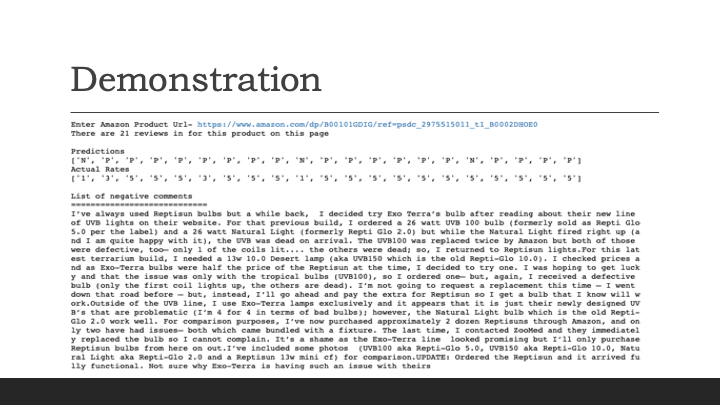
print('There are {} reviews in for this product on this page'.format(len(reviews)) )
#print(reviews)
return reviews, ratings
def punctuationRemover(p):
'''
Input: Takes a string. You may have to use str() to force it.
Removes all punctuation by checking every single character.
Output: Returns a string.
'''
punctuations = '''!()-[]{};:'"\,<>./?@#$%^&*_~1234567890'''
no_punctuations = ''
for words in p: # You may not have to loop this high
for char in words:
if char in punctuations:
no_punctuations = no_punctuations + ' '
if char not in punctuations:
no_punctuations = no_punctuations + char
return(no_punctuations)
def no_stopword (p):
token= ' '.join([word.lower() for word in p.split() if word.lower not in (stop)])
return token
def lemmatize_verbs(words):
"""Lemmatize verbs in list of tokenized words"""
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
lemmas = []
for word in words:
lemma = lemmatizer.lemmatize(word, pos='v')
lemmas.append(lemma)
return lemmas
def web_comments ():
"""Scraping and predicting multiple customer reviews from a website"""
review_list, ratings = scrape_reviews()
review_list_no_punc=[punctuationRemover(p) for p in review_list]
review_list_no_stop=[no_stopword(p) for p in review_list_no_punc]
test=review_list_no_stop
test_vektor=tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test)
test_vector=sequence.pad_sequences(test_vektor, maxlen=128)
prediction=model.predict([test_vector])
neg_com=[]
pos_com=[]
label=[int(round(prediction[0][0])) for prediction[0][0] in prediction]
labels=[]
for i in label:
if i==1:
labels.append('P')
else:
labels.append('N')
for i in label:
if i==0:
neg_com.append(review_list[i])
for i in label:
if i==1:
pos_com.append(review_list[i])
print ("")
print ("Predictions")
print(labels)
print ("Actual Rates")
print(ratings)
print ("")
print("List of negative comments")
print("============================")
for i in neg_com:
print (i)
print ("")

To try the model prediction on a product data on Amazon website, run the web-comments function. It will ask you to input any amazon product page url. Just copy and paste the url and press ENTER
References:
https://www.datasciencecentral.com/profiles/blogs/crisp-dm-a-standard-methodology-to-ensure-a-good-outcome
https://monkeylearn.com/blog/sentiment-analysis-of-product-reviews/